Interpolation Dialog Boxes
Inverse Distance Weighted

(a) Select Inverse Distance Weighted as interpolation method from drop down list.
(b) Enter the minimum number of neighbor stations nmin to interpolate a grid node.
(c) Enter the minimum number of neighbor stations nmax to interpolate a grid node.
(d) Enter the maximum distance maxdist (units in decimal degree) to define the search radius used to select the stations to interpolate a grid node.
(e) Check this box if you want to apply a spatial smoothing to the interpolated data. To define the block type and size, use the function
interpolation.options()on the R console, and change the argumentsblockTypeandblockSize. For more details on how the block is created, see the method CDT used for spatial smoothing.
Modified Shepard interpolation
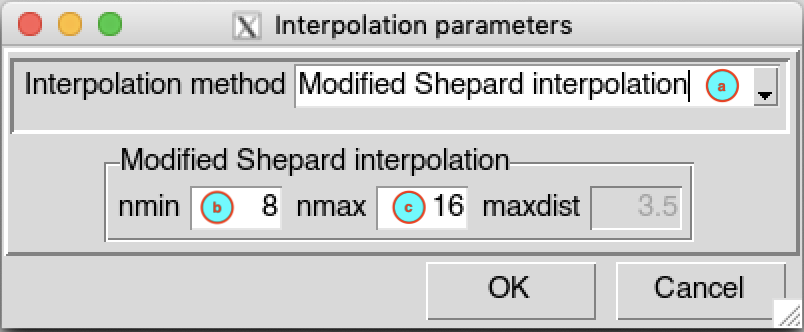
(a) Select Modified Shepard interpolation as interpolation method from drop down list.
(b) Enter the minimum number of neighbor stations nmin to interpolate a grid node.
(c) Enter the minimum number of neighbor stations nmax to interpolate a grid node.
Spheremap interpolation method
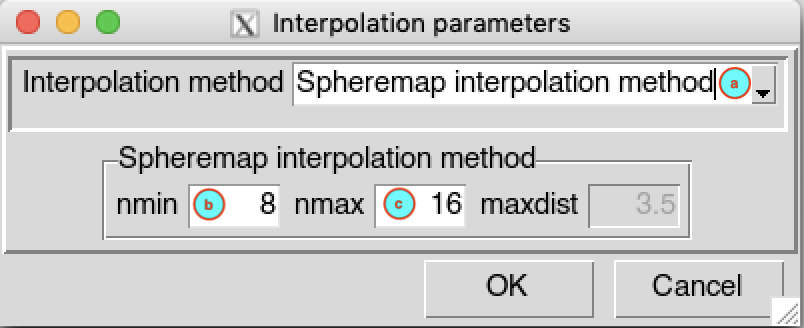
(a) Select Spheremap interpolation method as interpolation method from drop down list.
(b) Enter the minimum number of neighbor stations nmin to interpolate a grid node.
(c) Enter the minimum number of neighbor stations nmax to interpolate a grid node.
Ordinary Kriging
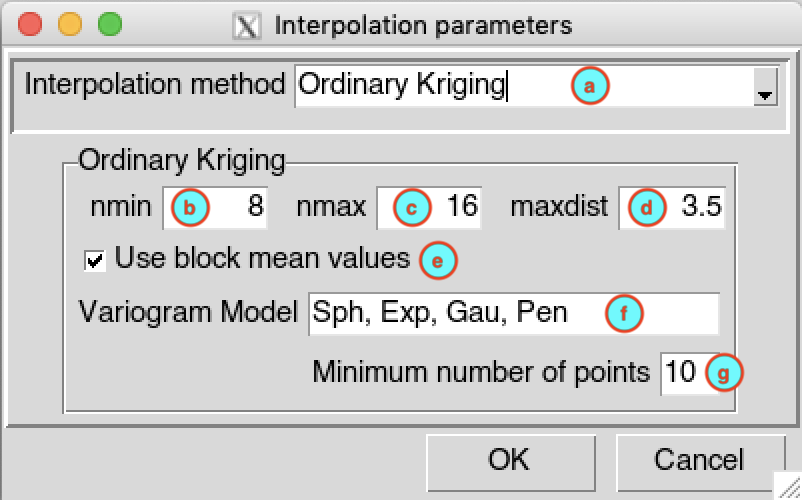
(a) Select Ordinary Kriging as interpolation method from drop down list.
(b) Enter the minimum number of neighbor stations nmin to interpolate a grid node.
(c) Enter the minimum number of neighbor stations nmax to interpolate a grid node.
(d) Enter the maximum distance maxdist (units in decimal degree) to define the search radius used to select the stations to interpolate a grid node.
(e) Check this box if you want to apply a spatial smoothing to the interpolated data. To define the block type and size, use the function
interpolation.options()on the R console, and change the argumentsblockTypeandblockSize. For more details on how the block is created, see the method CDT used for spatial smoothing.(f) Enter the list of candidate variogram models to be selected, the list must be separated by a comma. CDT use the function
autofitVariogramfrom the packageautomapto fit the variogram. The best fitting will be used for the interpolation. A list of all permitted variogram models is available by typingvgm()on the R console.(g) Enter the minimum number of stations with non-missing data to be used to compute the sample variogram.
Universal Kriging
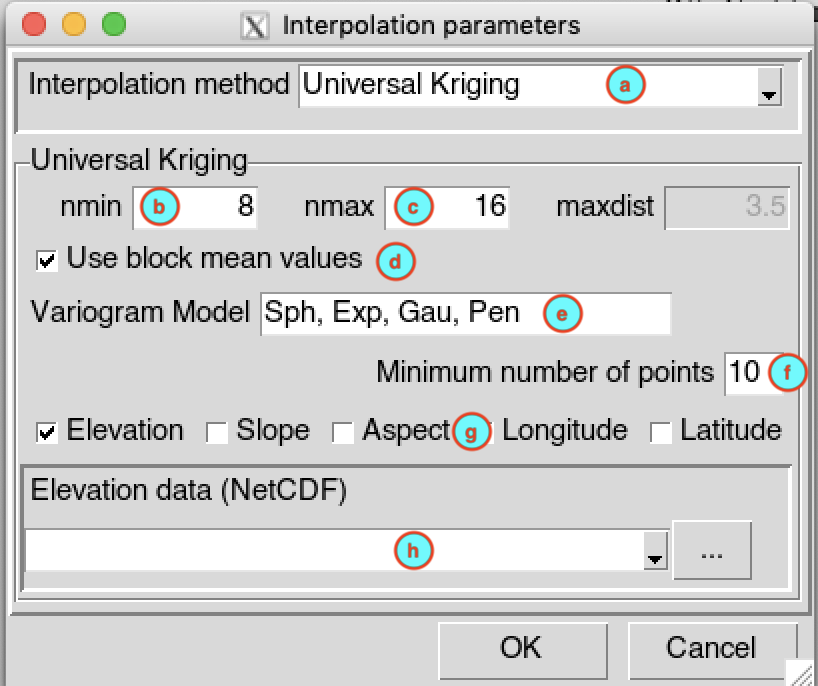
(a) Select Universal Kriging as interpolation method from drop down list.
(b) Enter the minimum number of neighbor stations nmin to interpolate a grid node.
(c) Enter the minimum number of neighbor stations nmax to interpolate a grid node.
(d) Check this box if you want to apply a spatial smoothing to the interpolated data. To define the block type and size, use the function
interpolation.options()on the R console, and change the argumentsblockTypeandblockSize. For more details on how the block is created, see the method CDT used for spatial smoothing.(e) Enter the list of candidate variogram models to be selected, the list must be separated by a comma. CDT use the function
autofitVariogramfrom the packageautomapto fit the variogram. The best fitting will be used for the interpolation. A list of all permitted variogram models is available by typingvgm()on the R console.(f) Enter the minimum number of stations with non-missing data to be used to compute the sample variogram.
(g) Check the auxiliaries variables to be used. You can choose between: elevation data; slope and aspect computed from the elevation data, see the function
terrainfrom therasterpackage fro more details; longitude and latitude.(h) In case you include elevation, slope and/or aspect, you have to provide the elevation data in NetCDF format, select it from the drop-down list if it is already loaded or open it from the browse button .
Nearest Neighbor
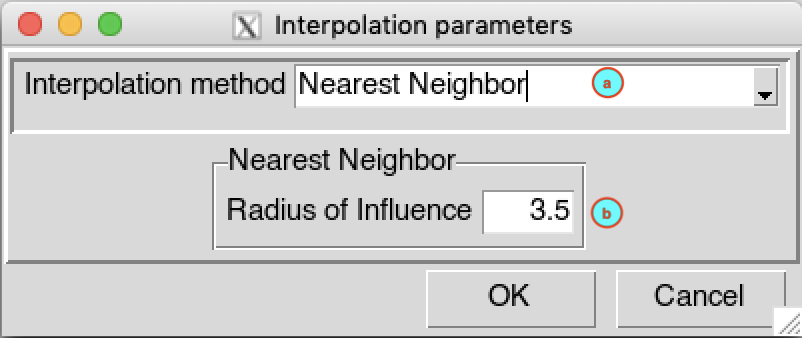
(a) Select Nearest Neighbor as interpolation method from drop down list.
(b) Enter the maximum distance (units in decimal degree) to define the search radius used to select the station to interpolate a grid node.
Nearest Neighbor with elevation - 3D

(a) Select Nearest Neighbor with elevation - 3D as interpolation method from drop down list.
(b) Enter the maximum distance (units in decimal degree) to define the search radius used to select the station to interpolate a grid node.
(c) Select the elevation data, in NetCDF format, from the drop-down list if it is already loaded or open it from the browse button .