Aggregation Parameters
Setting netCDF datasets parameters
This dialog box allows to set the date range, provide a sample file and change the filename format of the netCDF file.
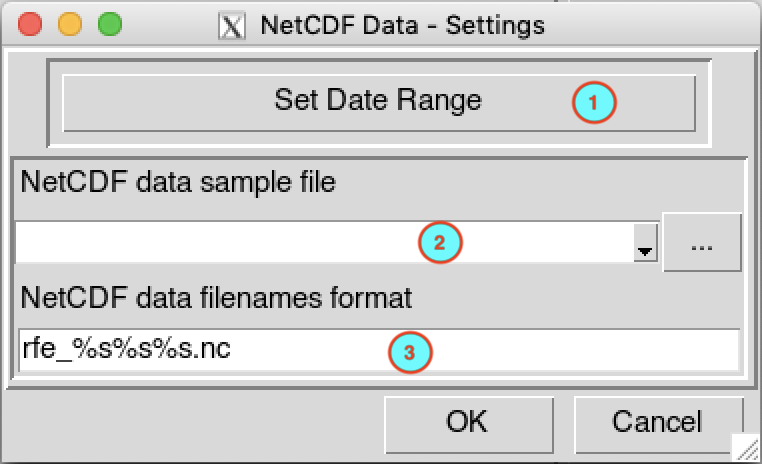
Set the date range of the data to be aggregated. See Setting date range for more details.
Provide a netCDF sample file. If the file is already opened in the Open Files list box, select it in the drop down list, if not, browse with the button
 in the right to open it.
in the right to open it.Change the filename format to conform with the netCDF files name. See NetCDF filename format for more details.
Aggregation parameters
This dialog box allows to select the function to use to aggregate the data and to set the minimum number of observations to compute the data.
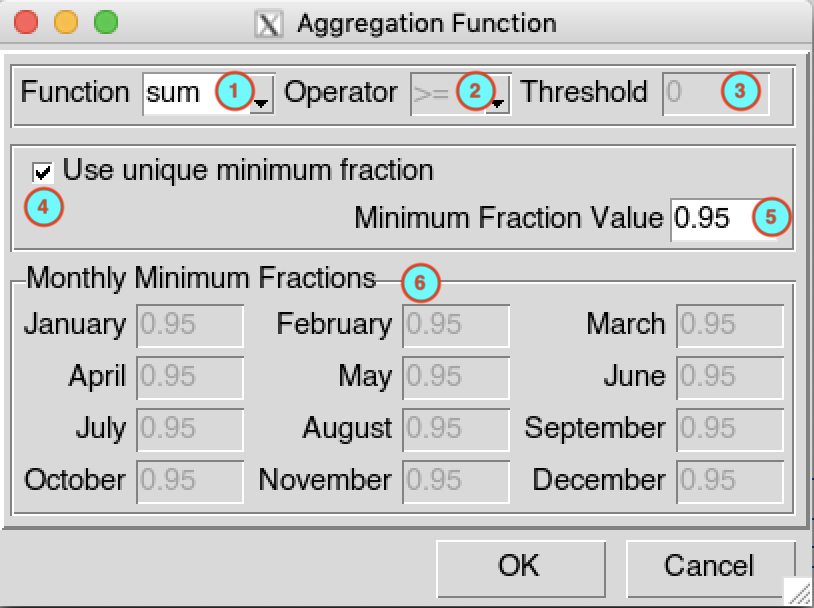
Select the function to use to aggregate the data. The list of functions varies depending on the menu where you click the button to open this dialog box. The available functions are as follow
- sum: computing the sum/total of a variable for a given time resolution
- mean: computing the mean/average of a variable for a given time resolution
- median: computing the median of a variable for a given time resolution
- var: computing the variance of a variable for a given time resolution
- sd: computing the standard variation of a variable for a given time resolution
- max: getting the maximum of a variable for a given time resolution
- min: getting the minimum of a variable for a given time resolution
- count: counting the number of occurrences where a variable is less/greater than a given threshold for a given time resolution
If the function you selected in (1) is count this drop down list will be activated, select the operator to be applied.
If the function you selected in (1) is count, enter here the threshold to be used.
Check this if you want to use a unique minimum number of observation to compute the value of the aggregated data, if the number of non missing observation is less than this value then the aggregated data is set to missing. Since the minimum number of value required to compute the aggregated data depends on the time resolution of the output data, then the value you have to specify here should be in fraction. For example, if you want to compute dekadal data from daily data, if the number of days in that dekad is 10, and you need at least 8 days of non missing observation to compute the value of the dekad, then the minimum fraction should be 8/10 = 0.8. In the same way, if you want to aggregate daily data to monthly, if the number of days in that month is 30, and you want to compute the value of the month using at least 21 days of non missing observation, then the minimum fraction should be set to 21/30 = 0.7.
Enter here the minimum fraction of available observations from the input data that must be present to aggregate the data (otherwise the aggregated value is missing).
If you unchecked (4) all the input fields will be activated allowing you to set a different minimum fraction of non missing observation for each month. This is very useful in the case of rainfall data. Indeed, if you have two distinct seasons: dry and rainy seasons, during the dry season there is no rain at all and the precipitation is no measured, you can set to 0 the minimum fraction of non missing observation. In other word, if there is no observation the value of the aggregated data will be 0 instead of missing.