IRI ENSO Forecast
IRI Technical ENSO Update and Model-Based Probabilistic ENSO Forecast
Published: November 20, 2017
Note: The SST anomalies cited below refer to the OISSTv2 SST data set, and not ERSSTv4. OISSTv2 is often used for real-time analysis and model initialization, while ERSSTv4 is used for retrospective official ENSO diagnosis because it is more homogeneous over time, allowing for more accurate comparisons among ENSO events that are years apart. During ENSO events, OISSTv2 often shows stronger anomalies than ERSSTv4, and during very strong events the two datasets may differ by as much as 0.5 C. Additionally, the ERSSTv4 may tend to be cooler than OISSTv2, because ERSSTv4 is expressed relative to a base period that is updated every 5 years, while the base period of OISSTv2 is updated every 10 years and so, half of the time, is based on a slightly older period and does not account as much for the slow warming trend in the tropical Pacific SST.
Recent and Current Conditions
In mid-November 2017, the NINO3.4 SST anomaly was in the weak La Niña category, and during the most recent weak was near the borderline of moderate La Niña. For October the SST anomaly was -0.46 C, near the borderline of ENSO-neutral and weak La Niña, and for August-October it was -0.35 C, in the cool ENSO-neutral range. The IRI’s definition of El Niño, like NOAA/Climate Prediction Center’s, requires that the SST anomaly in the Nino3.4 region (5S-5N; 170W-120W) exceed 0.5 C. Similarly, for La Niña, the anomaly must be -0.5 C or less. The climatological probabilities for La Niña, neutral, and El Niño conditions vary seasonally, and are shown in a table at the bottom of this page for each 3-month season. The most recent weekly anomaly in the Nino3.4 region was -1.1, qualifying for moderate La Niña for just that week. The pertinent atmospheric variables, including the upper and lower level zonal wind anomalies, have been showing patterns suggestive of La Niña, and he Southern Oscillation Index (SOI) has also been above average. Subsurface temperature anomalies across the eastern equatorial Pacific are somewhat below average. Given the current and recent SST anomalies, the subsurface profile and the La Niña patterns in most key atmospheric variables, an official diagnosis of La Niña is warranted and a La Niña Advisory has been issued.
Expected Conditions
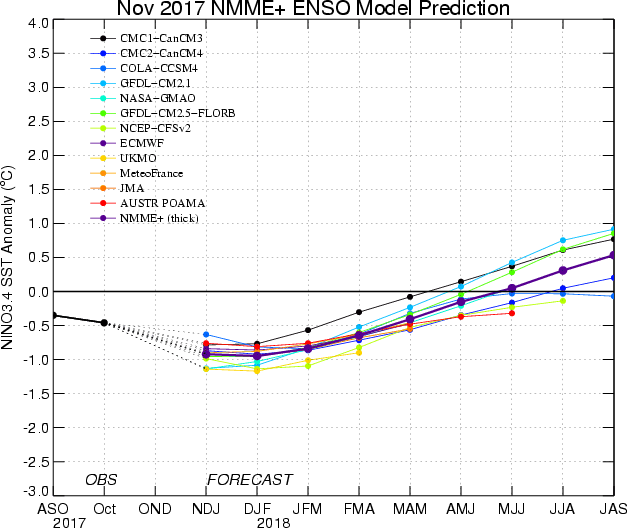
What is the outlook for the ENSO status going forward? The most recent official diagnosis and outlook was issued approximately one week ago in the NOAA/Climate Prediction Center ENSO Diagnostic Discussion, produced jointly by CPC and IRI; it stated that La Niña is favored for late fall and winter, with decidedly lower chances for ENSO-neutral. A La Niña Advisory was issued with that Discussion, following two months with a La Niña watch. The latest set of model ENSO predictions, from mid-November, now available in the IRI/CPC ENSO prediction plume, is discussed below. Those predictions suggest that the SST has the greatest chance for staying in the weak La Niña range for November-January through January-March 2017, with a lower but non-negligible probability for ENSO-neutral during that period.
As of mid-November, about 75% of the dynamical or statistical models predicts La Niña conditions for the initial Nov-Jan 2017-18 season, dropping a bit to 68% for the Jan-Mar 2018 season. During this period, no model predicts El Niño conditions, so that the remaining probability is only for neutral conditions. At lead times of 3 or more months into the future, statistical and dynamical models that incorporate information about the ocean’s observed subsurface thermal structure generally exhibit higher predictive skill than those that do not. For the Feb-Apr 2018 season, among models that do use subsurface temperature information, 38% of models predicts neutral conditions and 62% predicts La Niña conditions. For all models, at longer lead times beginning with Mar-May 2018, predictions for ENSO-neutral conditions dominate, with probabilities of 85% or more for Mar-May to May-Jul. At the end of the forecast range, Jun-Aug and Jul-Sep, the probability for El Niño rises to nearly 30% and La Niña probabilities decrease to near zero, leaving just over 70% for neutral.
Note – Only models that produce a new ENSO prediction every month are included in the above statement.
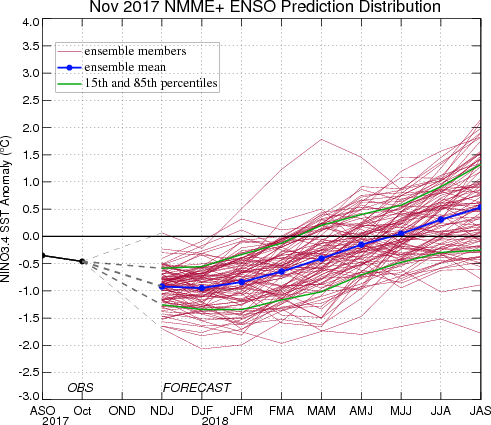
Caution is advised in interpreting the distribution of model predictions as the actual probabilities. At longer leads, the skill of the models degrades, and skill uncertainty must be convolved with the uncertainties from initial conditions and differing model physics, leading to more climatological probabilities in the long-lead ENSO Outlook than might be suggested by the suite of models. Furthermore, the expected skill of one model versus another has not been established using uniform validation procedures, which may cause a difference in the true probability distribution from that taken verbatim from the raw model predictions.
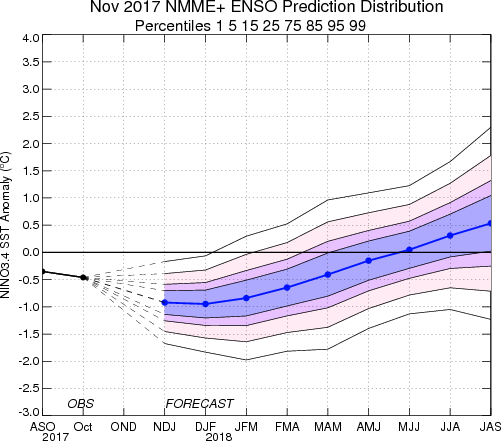
An alternative way to assess the probabilities of the three possible ENSO conditions is more quantitatively precise and less vulnerable to sampling errors than the categorical tallying method used above. This alternative method uses the mean of the predictions of all models on the plume, equally weighted, and constructs a standard error function centered on that mean. The standard error is Gaussian in shape, and has its width determined by an estimate of overall expected model skill for the season of the year and the lead time. Higher skill results in a relatively narrower error distribution, while low skill results in an error distribution with width approaching that of the historical observed distribution. This method shows probabilities for La Niña between 70 and 75% for Nov-Jan and Dec-Feb, decreasing thereafter to 45% for Feb-Apr and to 15-20% from Apr-Jun through Jul-Sep. Probabilities for neutral conditions begin at 25% for Nov-Jan, first exceed 50% in Feb-Apr, and peak around 75% in Apr-June, after which it drops to less than 50% for Jul-Sep as El Niño probabilities rise to 38% after having been less than 10% through Apr-Jun. A plot of the probabilities generated from this most recent IRI/CPC ENSO prediction plume using the multi-model mean and the Gaussian standard error method summarizes the model consensus out to about 10 months into the future. The same cautions mentioned above for the distributional count of model predictions apply to this Gaussian standard error method of inferring probabilities, due to differing model biases and skills. In particular, this approach considers only the mean of the predictions, and not the total range across the models, nor the ensemble range within individual models.
In summary, the probabilities derived from the models on the IRI/CPC plume describe, on average, a preference for weak La Niña conditions from Nov-Jan 2017-18 to Jan-Mar 2018, with neutral regaining highest probability status from Feb-Apr through the end of the forecast period in late summer 2018. Chances for El Niño are very small through Apr-Jun 2018, rising to near-climatological probabilities for May-Jul and slightly higher for Jun-Aug and Jul-Sep 2018. A caution regarding this latest set of model-based ENSO plume predictions, is that factors such as known specific model biases and recent changes that the models may have missed will be taken into account in the next official outlook to be generated and issued early next month by CPC and IRI, which will include some human judgment in combination with the model guidance.
Climatological Probabilities
| Season |
La Niña |
Neutral |
El Niño |
| DJF |
36% |
30% |
34% |
| JFM |
34% |
38% |
28% |
| FMA |
28% |
49% |
23% |
| MAM |
23% |
56% |
21% |
| AMJ |
21% |
58% |
21% |
| MJJ |
21% |
56% |
23% |
| JJA |
23% |
54% |
23% |
| JAS |
25% |
51% |
24% |
| ASO |
26% |
47% |
27% |
| SON |
29% |
39% |
32% |
| OND |
32% |
33% |
35% |
| NDJ |
35% |
29% |
36% |
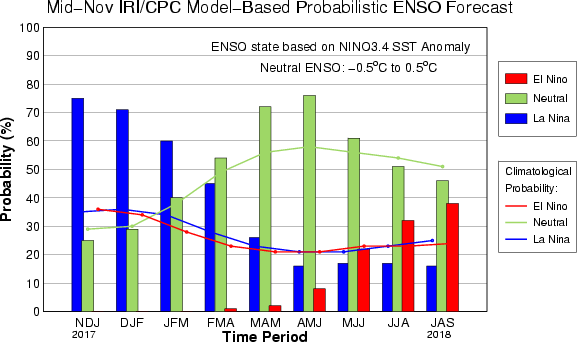
IRI/CPC Mid-Month Model-Based ENSO Forecast Probabilities
| Season |
La Niña |
Neutral |
El Niño |
| NDJ 2017 |
75% |
25% |
0% |
| DJF 2018 |
71% |
29% |
0% |
| JFM 2018 |
60% |
40% |
0% |
| FMA 2018 |
45% |
54% |
1% |
| MAM 2018 |
26% |
72% |
2% |
| AMJ 2018 |
16% |
76% |
8% |
| MJJ 2018 |
17% |
61% |
22% |
| JJA 2018 |
17% |
51% |
32% |
| JJA 2018 |
16% |
46% |
38% |