IRI ENSO Forecast
IRI Technical ENSO Update
Published: December 19, 2013
Recent and Current Conditions
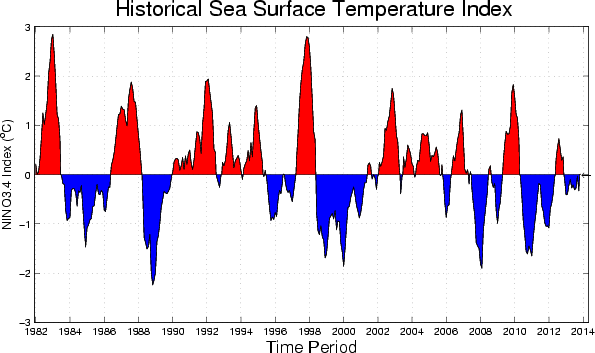
The SST anomaly in the Nino3.4 region has been in the neutral range lately, through mid-December 2013. For November 2013 the Nino3.4 SST anomaly was 0.01 C, indicative of neutral ENSO conditions, and for September-November it was -0.13 C. The IRI’s definition of El Niño, like NOAA/Climate Prediction Center’s, requires that the SST anomaly in the NINO3.4 region (5S-5N; 170W-120W) exceed 0.5 C. Similarly, for La Niña, the anomaly must be -0.5 C or less. The climatological probabilities for La Niña, neutral, and El Niño conditions vary seasonally, and are shown in a table at the bottom of this page for each 3-month season. The most recent weekly SST anomaly in the NINO3.4 region was 0.0 C, indicating neutral ENSO-related SST conditions in the tropical Pacific; this is virtually identical to the 0.01 C level observed in November.
Expected Conditions
What is the outlook for the ENSO status going forward? The most recent official diagnosis and outlook was issued earlier this month in the NOAA/Climate Prediction Center ENSO Diagnostic Discussion, produced jointly by CPC and IRI; it called for a high likelihood of neutral ENSO conditions enduring through winter 2013-14 and into spring 2014, with probabilities of El Niño or La Niña each less than 30% until Apr-Jun 2014 when El Niño probabilities rise above that level but stay less than 50% through summer 2014. The latest set of model ENSO predictions, from mid-December, now available in the IRI/CPC ENSO prediction plume, is discussed below. Currently, Nino3.4 SST anomalies are in the ENSO-neutral range, are slightly above average in the far western and west-central part of the basin and continue to be slightly below average in the eastern quarter of the basin. Subsurface temperature anomalies across the central and eastern equatorial Pacific have been slightly above average since mid-May, and have now become more clearly and strongly positive. In the atmosphere, the basin-wide sea level pressure pattern (e.g. the SOI), and the low-level zonal winds have been approximately average across much of the basin, although enhanced trades are observed in the western part of the basin. The upper level zonal winds are also mainly near-average across the tropical Pacific. Anomalous convection (as measured by OLR) has generally been negative in the west-central tropical Pacific, and positive in the far western part of the basin and in Indonesia. Together, these features reflect ENSO-neutral conditions.
As of mid-December, 4% of the set of dynamical and statistical models models predicts weak La Niña SST conditions for the Dec-Feb 2013-14 season, 0% predicts El Niño conditions, and 96% indicates neutral ENSO. At lead times of 3 or more months into the future, statistical and dynamical models that incorporate information about the ocean’s observed subsurface thermal structure generally exhibit higher predictive skill than those that do not. For the Mar-May 2014 season, among models that do use subsurface temperature information, 76% predicts ENSO-neutral SSTs, 24% predicts El Niño conditions and none predicts La Niña conditions. For all model types, the probability for neutral ENSO conditions is above 90% for Dec-Feb 2013-14 and Jan-Mar 2014, above 80% through Apr-Jun 2014, and 67%-73% for May-Jul through Aug-Oct 2014 at the end of the forecast period. Probabilities for El Niño are below 20% through Apr-Jun 2014, and rise to approxiately 30% from May-Jul through Aug-Oct.
Note – Only models that produce a new ENSO prediction every month are included in the above statement.
Caution is advised in interpreting the distribution of model predictions as the actual probabilities. At longer leads, the skill of the models degrades, and skill uncertainty must be convolved with the uncertainties from initial conditions and differing model physics, leading to more climatological probabilities in the long-lead ENSO Outlook than might be suggested by the suite of models. Furthermore, the expected skill of one model versus another has not been established using uniform validation procedures, which may cause a difference in the true probability distribution from that taken verbatim from the raw model predictions.
An alternative way to assess the probabilities of the three possible ENSO conditions is more quantitatively precise and less vulnerable to sampling errors than the categorical tallying method used above. This alternative method uses the mean of the predictions of all models on the plume, equally weighted, and constructs a standard error function centered on that mean. The standard error is Gaussian in shape, and has its width determined by an estimate of overall expected model skill for the season of the year and the lead time. Higher skill results in a relatively narrower error distribution, while low skill results in an error distribution with width approaching that of the historical observed distribution. This method shows probabilities for La Niña at 1% for Dec-Feb 2013-14, remaining at 10% or less through the end of the forecast period in Aug-Oct 2014. Model probabilities for ENSO-neutral conditions are more than 90% from Dec-Feb 2013-14 to Jan-Mar 2014, dropping steadily during northern spring 2014 to become slightly less than 50% from Jun-Aug through the end of the forecast period in Aug-Oct 2014. Probabilities for El Niño are below 10% from Dec-Feb 2013-14 to Feb-Apr 2014, thereafter steadily increasing to exceed 30% by May-Jul 2014 and to between 40% and 50% from Jun-Aug to Aug-Oct 2014 (maximizing at 45% for both Jul-Sep). It is clear that the models collectively favor neutral ENSO conditions into northern spring 2014; then by Jun-Aug El Niño probabilities become more competitive with ENSO-neutral probabilities, until they are approximately equally likely for Jul-Sep and Aug-Oct 2014. A plot of the probabilities generated from this most recent IRI/CPC ENSO prediction plume using the multi-model mean and the Gaussian standard error method summarizes the model consensus out to about 10 months into the future. The same cautions mentioned above for the distributional count of model predictions apply to this Gaussian standard error method of inferring probabilities, due to differing model biases and skills. In particular, this approach considers only the mean of the predictions, and not the total range across the models, nor the ensemble range within individual models.
The probabilities derived from the models on the IRI/CPC plume describe, on average, maintenance of neutral ENSO conditions into northern spring 2014. The possibility of El Niño development is seen starting Jun-Aug 2014, but the objective model-based probabilities for El Niño still remain below 50% for Jun-Aug through Aug-Oct 2014. A caution regarding this latest set of model-based ENSO plume predictions, is that factors such as known specific model biases and recent changes that the models may have missed will be taken into account in the next official outlook to be generated and issued in early October by CPC and IRI, which will include some human judgement in combination with the model guidance.
Using the 0.5 C thresholds, the climatological probabilities of La Nina, neutral, and El Nino conditions for each 3-month season are as follows:
Climatological Probabilities
| Season |
La Niña |
Neutral |
El Niño |
| DJF |
37% |
28% |
35% |
| JFM |
34% |
37% |
29% |
| FMA |
30% |
48% |
22% |
| MAM |
26% |
54% |
20% |
| AMJ |
24% |
54% |
22% |
| MJJ |
25% |
51% |
24% |
| JJA |
25% |
50% |
25% |
| JAS |
27% |
46% |
27% |
| ASO |
29% |
40% |
31% |
| SON |
32% |
34% |
34% |
| OND |
34% |
31% |
35% |
| NDJ |
37% |
27% |
36% |
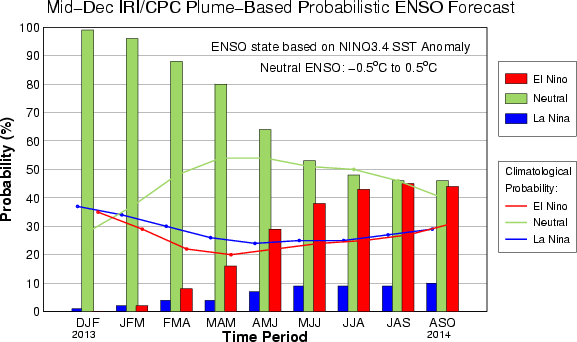
IRI/CPC Mid-Month Plume-Based ENSO Forecast Probabilities
| Season |
La Niña |
Neutral |
El Niño |
| DJF 2014 |
1% |
99% |
~0% |
| JFM 2014 |
2% |
96% |
2% |
| FMA 2014 |
4% |
88% |
8% |
| MAM 2014 |
4% |
80% |
16% |
| AMJ 2014 |
7% |
64% |
29% |
| MJJ 2014 |
9% |
53% |
38% |
| JJA 2014 |
9% |
48% |
43% |
| JAS 2014 |
9% |
46% |
45% |
| ASO 2014 |
10% |
46% |
44% |