IRI ENSO Forecast
IRI Technical ENSO Update
Published: December 19, 2022
Note: The SST anomalies cited below refer to the OISSTv2 SST data set, and not ERSSTv5. OISSTv2 is often used for real-time analysis and model initialization, while ERSSTv5 is used for retrospective official ENSO diagnosis because it is more homogeneous over time, allowing for more accurate comparisons among ENSO events that are years apart. These two products may differ, particularly during ENSO events. The difference between the two datasets may be as much as 0.5 °C. Additionally in some years, the ERSSTv5 may tend to be cooler than OISSTv2 in the context of warming trends, because ERSSTv5 is expressed relative to a base period that is updated every 5 years, while the base period of OISSTv2 is updated every 10 years. In February 2021, both datasets were updated to reflect the 1991-2020 climatology period.
Recent and Current Conditions
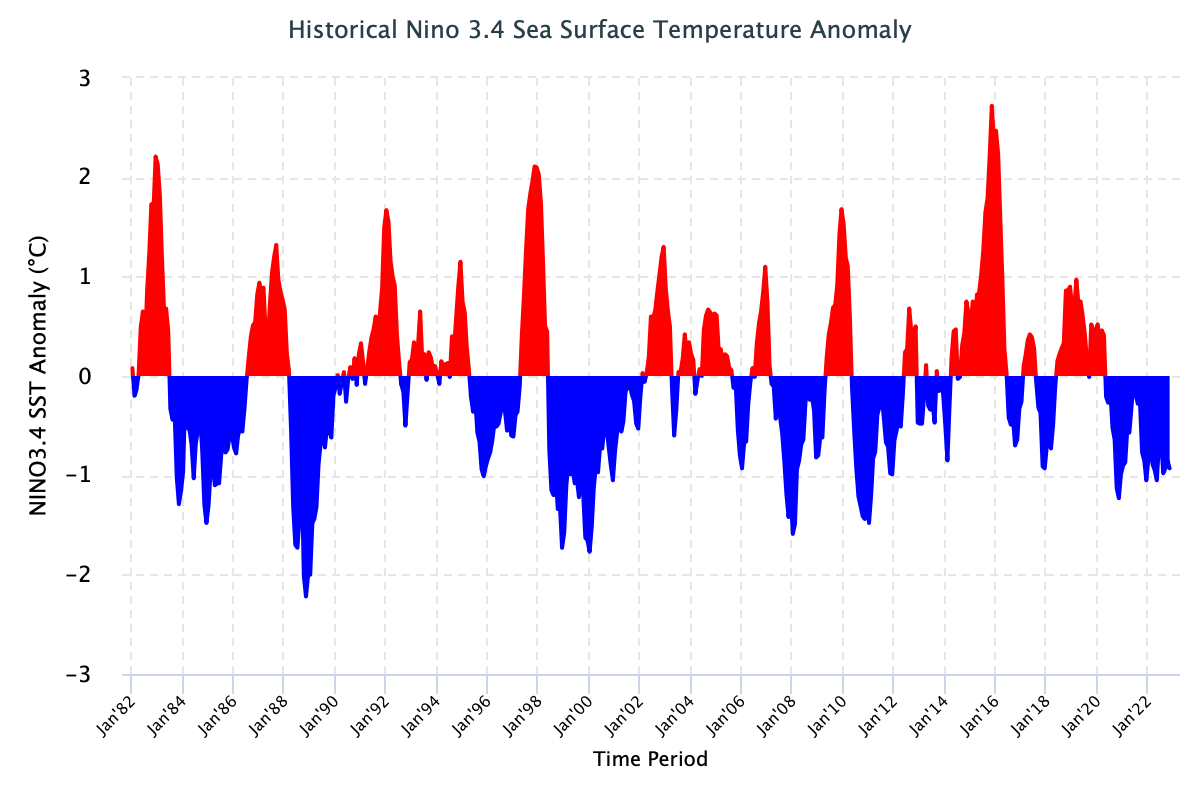
The SST anomaly for NINO3.4 during the Sep-Nov season was -0.90 °C, and for the month of November it was -0.93 °C. The most recent weekly (14 Dec 2022) anomaly in the NINO3.4 region was -0.9 °C, indicating persistent La Niña conditions in the tropical Pacific. The IRI’s definition of El Niño, like NOAA/Climate Prediction Center’s, requires that the SST anomaly in the NINO3.4 region (5S-5N; 170W-120W) exceed 0.5 °C. Similarly, for La Niña, the anomaly must be -0.5 °C or colder.
Many of the key atmospheric variables remain indicative of La Niña conditions, such as the traditional and equatorial Southern Oscillation Indices are positive, (as of 17 December, 2022, last observed value was +10.6), the low-level easterly winds are stronger than normal across the central-eastern Pacific, while upper-level wind anomalies remain westerly across the tropical Pacific, anomalously dry conditions have been observed over the central and western Pacific Ocean. For the ocean, subsurface temperature anomalies in the western and central (west of 130o W) equatorial Pacific are warmer than average (at the depth of 100 to 250 m), while colder subsurface temperatures are located eastern side (east of 130o W) of the basin (surface to 150 m). In summary, current conditions still indicate a borderline La Niña that is now dissipating.
Expected Conditions
Note – Only models that produce a new ENSO prediction every month are considered in this statement.
What is the outlook for the ENSO status going forward?
El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Diagnostic Discussion issued on 08 December 2022 by the Climate Prediction Center/NCEP/NWS indicates a continuation of the current La Niña event.
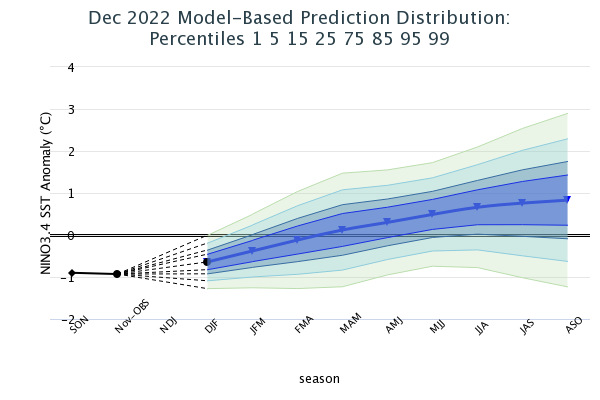
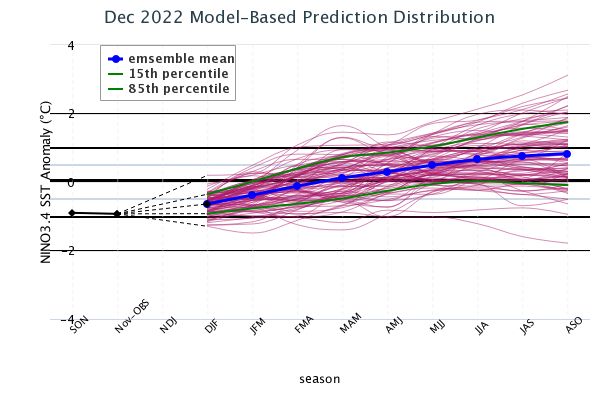
The latest set of ENSO prediction models from mid-December are now available in the IRI ENSO prediction plume. These are used to assess the probabilities of the three ENSO categories by using the average value of the NINO3.4 SST anomaly predictions from all models in the plume, equally weighted. Please note that the BCC model was not factored into these probabilities, even though it appears in the ENSO plume-of-models graphic. A standard Gaussian error is imposed over that average forecast, and its width is determined by an estimate of overall expected model skill for the season of the year and the lead time. Higher skill results in a relatively narrower error distribution, while low skill results in an error distribution with width approaching that of the historical observed distribution.
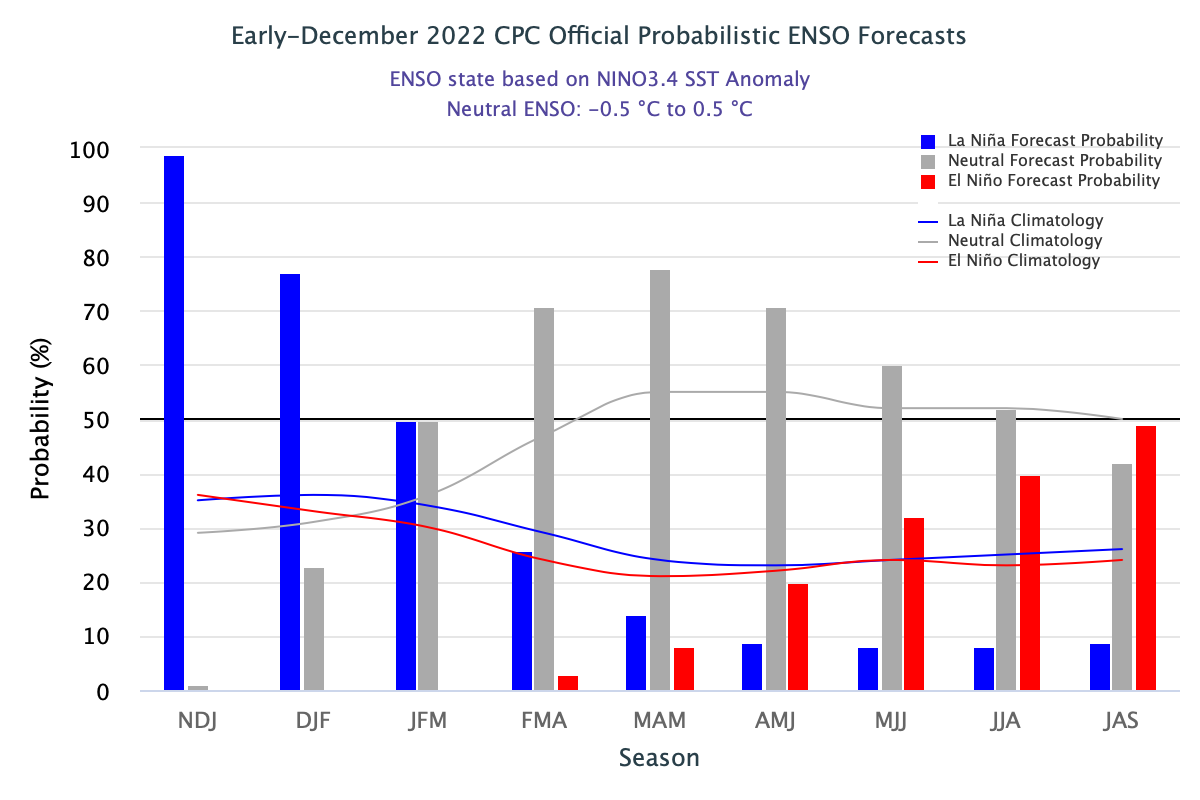
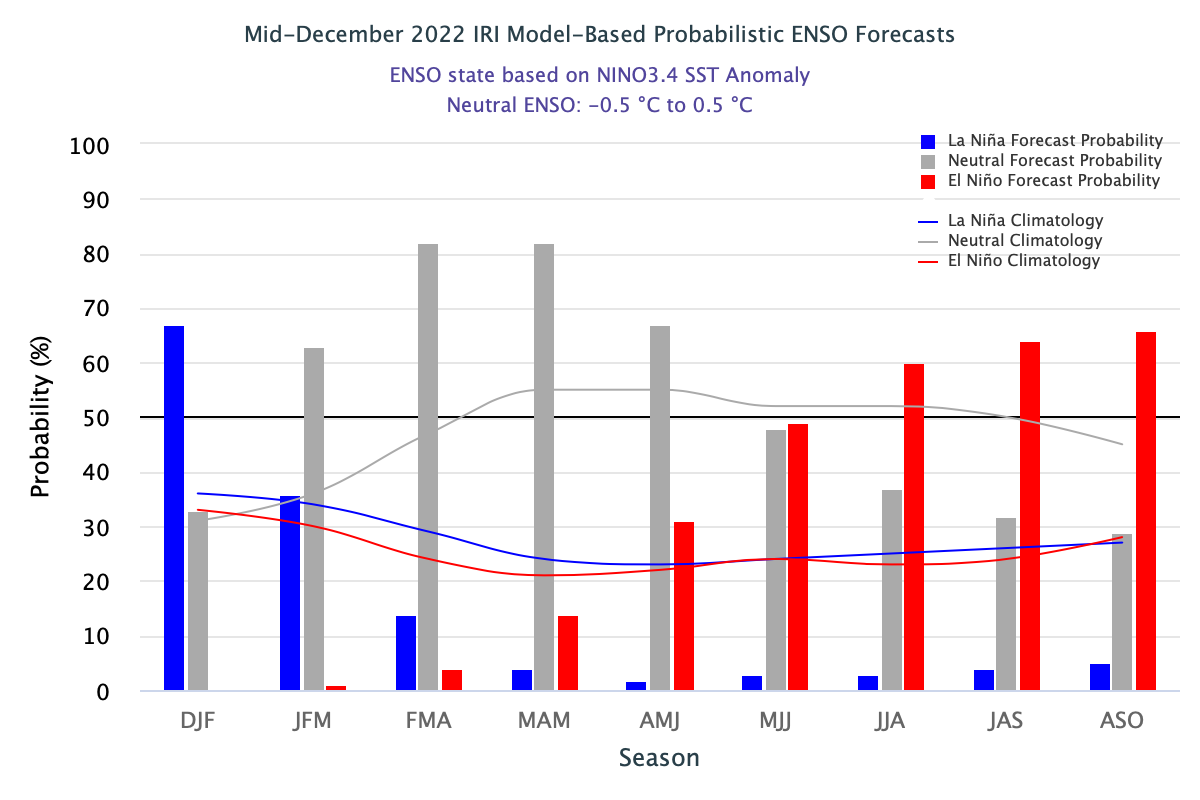
A large number (11 out of 18) of the models in the plume predict SSTs to transition to ENSO-neutral conditions in Jan-Mar 2023. The predicted probability of ENSO-neutral during Jan-Mar is 63%, while that of the La Ni
ña category is 36%. Going forward, ENSO-neutral conditions are highly favored for next three seasons (82% in Feb-Apr, 82% in Mar-May, 67% in Apr-Jun). According to the mid-month forecast, ENSO-neutral (48% chance) and El Niño (49% chance) conditions are equally likely during May-Jul 2023, with El Niño conditions becoming the most likely category in subsequent three seasons with the forecast probabilities are in the range of 60-66% (60% in Jun-Aug, 64% in Jul-Sep, 66% in Aug-Oct, 2023). A plot of the probabilities summarizes the forecast evolution. The climatological probabilities for La Niña, ENSO-neutral, and El Niño conditions vary seasonally, and are shown in a table at the bottom of this page for each 3-month season.
Caution is advised in interpreting the forecast distribution from the Gaussian standard error as the actual probabilities, due to differing biases and performance of the different models. In particular, this approach considers only the mean of the predictions, and not the total range across the models, nor the ensemble range within individual models. At longer leads, the skill of the models degrades, and uncertainty in skill must be convolved with the uncertainties from initial conditions and differing model physics, which leads to more climatological probabilities in the long-lead ENSO Outlook than might be suggested by the suite of models. Furthermore, the expected skill of one model versus another has not been established using uniform validation procedures, which may cause a difference in the true probability distribution.
In summary, the probabilities derived from the models in the IRI ENSO forecast plume indicate a preference for the discontinuation of the current La Niña event during Jan-Mar, while ENSO-neutral conditions are most likely (with 63% chance in Jan-Mar) and thereafter till May-Jul 2023. The likelihood of El Niño development remains low during boreal winter and spring of 2023, but gradually increases to become a dominant category in boreal summer of 2023, though with a significant amount of uncertainty beyond boreal spring.
A caution regarding the model-based ENSO plume predictions released mid-month, is that factors such as known specific model biases and recent changes in the tropical Pacific that the models may have missed, are not considered. This approach is purely objective. Those issues are taken into account in the official outlooks, which are generated and issued early in the month by CPC, and which will include some human judgment in combination with the model guidance.
| Season |
La Niña |
Neutral |
El Niño |
| DJF |
67 |
33 |
0 |
| JFM |
36 |
63 |
1 |
| FMA |
14 |
82 |
4 |
| MAM |
4 |
82 |
14 |
| AMJ |
2 |
67 |
31 |
| MJJ |
3 |
48 |
49 |
| JJA |
3 |
37 |
60 |
| JAS |
4 |
32 |
64 |
| ASO |
5 |
29 |
66 |