Automatic Weather Station Data Tool
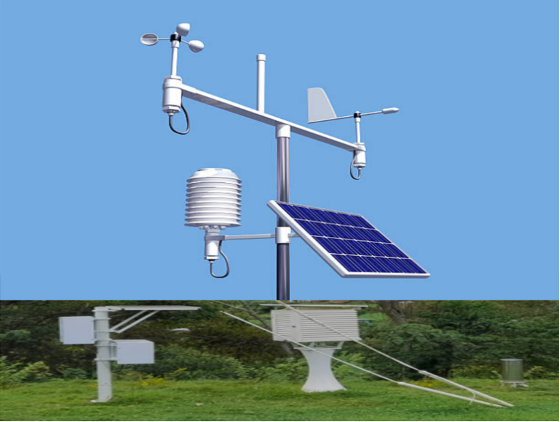

The data collected by these different AWS systems are in different formats and may sit on different computers. Although there are applications that come with each AWS network to access and visualize AWS data, access to the data is still done manually and station by station. This complicates data access, processing, and use.

In addition, data from the different AWS networks is in different formats, which makes it even more difficult to analyze all the data without additional tools or applications that can convert the data into a common format and combine the data from the different networks. As a result, accessing, processing, and using these data has been a major impediment to the use of data from these varieties of AWS.
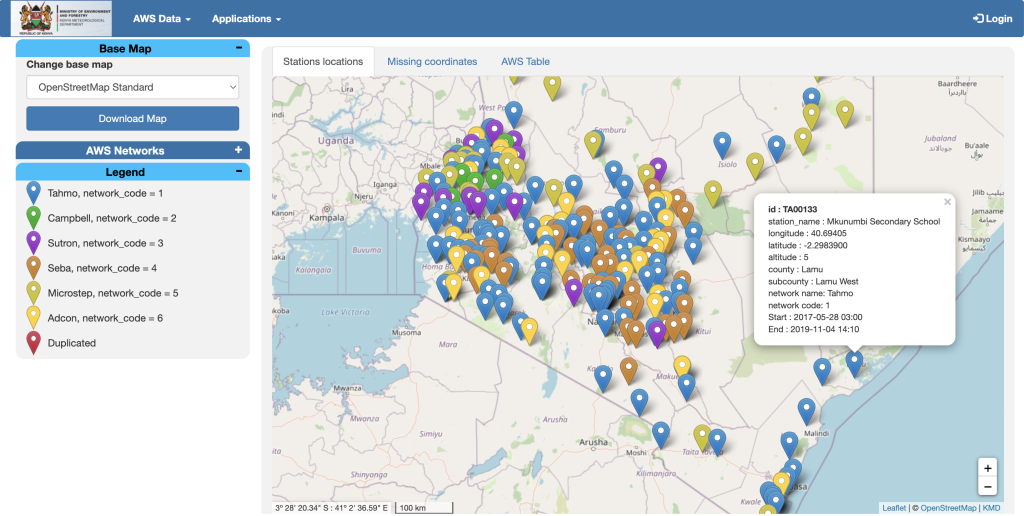
The Automatic Weather Station Data Tool (ADT) is a web-based application developed to alleviate these and other related challenges with access and use of AWS data. ADT has an easy-to-use graphical user interface and enables NMS to access, process, quality control, analyze, visualize, and disseminate data from different AWS systems in one place.
The main components of ADT include the following:
- Fetching data from different AWS network systems;
- Data pre-processing and quality control;
- Creating a unified database that allows storage of quality-checked data from different AWS networks;
- Data processing and analysis; and
- Data visualization and dissemination.
Acknowledgements
Funding for the initial development and design of ADT was generously provided from the American People through the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) through the “Climate Services for Agriculture: Empowering Farmers to
Manage Risk and Adapt to a Changing Climate in Rwanda” project.
Continued development and implementation of ADT has been provided by the Accelerating Impacts of CGIAR Climate Research for Africa (AICCRA). AICCRA is a project that helps deliver a climate-smart African future driven by science and innovation in agriculture. It is led by the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT and supported by a grant from the International Development Association (IDA) of the World Bank.
It is also supported through the Climate Risk and Early Warning Systems (CREWS) initiative of the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).

You must be logged in to post a comment.