| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ENSO Quick Look 21 November 2013Note on interpreting model forecastsThe following graph and table show forecasts made by dynamical and statistical models for SST in the Nino 3.4 region for nine overlapping 3-month periods. Note that the expected skills of the models, based on historical performance, are not equal to one another. The skills also generally decrease as the lead time increases. Thirdly, forecasts made at some times of the year generally have higher skill than forecasts made at other times of the year--namely, they are better when made between June and December than when they are made between February and May. Differences among the forecasts of the models reflect both differences in model design, and actual uncertainty in the forecast of the possible future SST scenario. Table 1. Forecast SST Anomalies (deg C) in the Nino 3.4 Region
Discussion of current forecastsMost of the set of dynamical and statistical model predictions issued during late October and early November 2013 predict neutral ENSO conditions through the rest of 2013 and into early 2014, with a warming tendency during northern spring and summer 2014. Development of weak El Nino conditions appears possible by the middle of 2014. In the most recent week, the SST anomaly in the Nino3.4 region was 0.0C. Based on the multi-model mean predictions, and the expected skill of the models by start time and lead time, the probabilities (X100) for La Nina, neutral and El Nino conditions (using -0.5C and 0.5C thresholds) over the coming 9 seasons are:
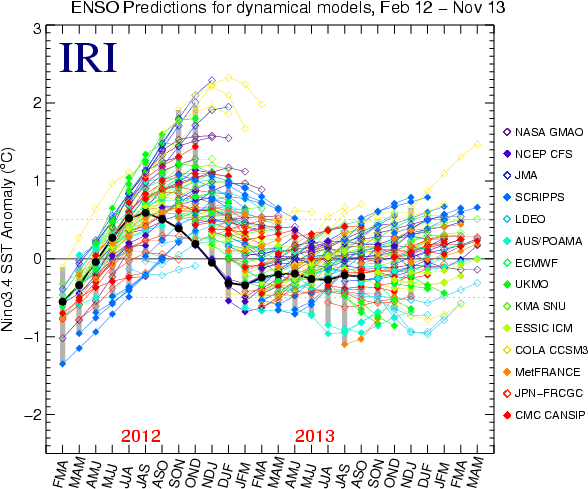
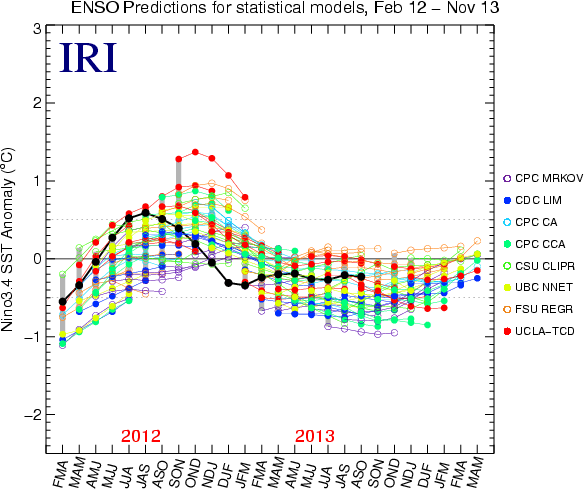
Summary of forecasts issued over last 22 monthsThe following plots show the model forecasts issued not only from the current month (as in the plot above), but also from the 21 months previous to this month. The observations are also shown up to the most recently completed 3-month period. The plots allow comparison of plumes from the previous start times, or examination of the forecast behavior of a given model over time. The first plot shows forecasts for dynamical models, the second for statistical models, and the third for all models. For less difficult readability, forecasts are shown to a maximum of only the first five lead times. Below the third plot, we provide a mechanism for highlighting the forecasts of one model at a time against a background of more lightly colored lines for all other models. Individual Model View over last 22 monthsView individual models here. Additional information on ModelsNotes on the dataOnly models producing forecasts on a monthly basis are included. This means that some models whose forecasts appear in the Experimental Long-Lead Forecast Bulletin (produced by COLA) do not appear in the table. The SST anomaly forecasts are for the 3-month periods shown, and are for the Nino 3.4 region (120-170W, 5N-5S). Often, the anomalies are provided directly in a graph or a table by the respective forecasting centers for the Nino 3.4 region. In some cases, however, they are given for 1-month periods, for 3-month periods that skip some of the periods in the above table, and/or only for a region (or regions) other than Nino 3.4. In these cases, the following means are used to obtain the needed anomalies for the table:
The anomalies shown are those with respect to the base period used to define the normals, which vary among the groups producing model forecasts. They have not been adjusted to anomalies with respect to a common base period. Discrepancies among the climatological SST resulting from differing base periods may be as high as a quarter of a degree C in the worst cases. Forecasters are encouraged to use the standard 1971-2000 period as the base period, or a period not very different from it. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||