| |||||
IRI NET ASSESSMENT FORECAST
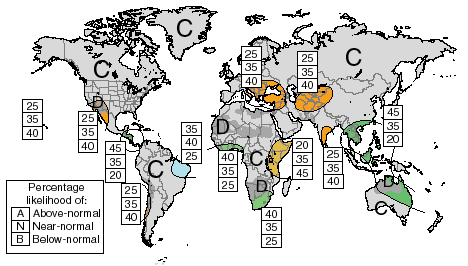
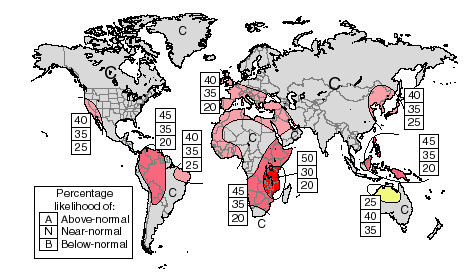
PRECIPITATION OUTLOOK The Outlook for April through June 1999 can also be found at http://iri.columbia.edu/forecast/net_asmt. Maps are given showing expected precipitation probabilities in tercile classes. The maps indicate probabilities that seasonal precipitation will fall into the wettest third of the years (top number), the middle third of years (middle number) or the driest third of the years (bottom). An outlook of climatology "C" indicates equal probabilities in each class i.e.; there is no basis for favoring the forecast of any particular category. Areas marked "D" experience a pronounced dry season during the forecast period, typically receiving less than 15% of their annual precipitation total during this three-month period. Boundaries between sub-regions should be considered transition zones, and their location considered to be only qualitatively correct. METHODS The following procedures and information were used to prepare this Climate Outlook: 1) Coupled ocean-atmosphere model predictions of tropical Pacific SST Particularly heavy weighting has been given to the NOAA /NCEP, Climate Modeling Branch coupled model which suggests continuation of moderate La Niña conditions, slowly decaying during the forecast period, with the persistence of strong positive sea-surface temperature anomalies near Indonesia, 2) statistical forecasts of Indian Ocean and Atlantic Ocean sea surface temperature, 3) Atmospheric global circulation model (GCM) predictions response to the present and predicted SST patterns, 4) Statistical analyses, 5) Appropriate Regional Climate Outlook Forum consensus guidance. The procedures, models, and data used to derive this Climate Outlook may be somewhat different from those used by National Meteorological Services in particular regions and may differ from the official forecasts issued in those areas. This Climate Outlook is dependent on the quality of the SST predictions. For the tropical Pacific, these predictions can be expected to provide useful information, but there is some uncertainty concerning the evolution of SSTs. This spread in predictions is a primary source of uncertainty in the Outlook provided here. It is stressed that the current status of seasonal-to-interannual climate forecasting allows prediction of spatial and temporal averages, and does not fully account for all factors that influence regional and national climate variability. This Outlook is relevant only to seasonal time scales and relatively large areas; local variations should be expected. For further information concerning this and other guidance products, users are strongly advised to contact their National Meteorological Services. TEMPERATURE OUTLOOK
|